
Health supplement trials -
Additionally, this aids teams in giving enough training and allocating the right resources during the initial startup phase. Clinical research is particularly challenging for dietary supplements.
Designing clinical studies with clinically relevant endpoints in mind is a good idea. One needs to pay close attention to transferring preclinical findings to the clinical setting.
Credevo provides end-to-end solutions, from conducting clinical trials to registering your food supplements globally. Provide your required details in the form to connect with us and explore our services. Request A Quote Please enable JavaScript in your browser to complete this form.
Aug 15 0. What are food supplements? Forms of food supplements pills tablets capsules liquid gummies powders drinks energy bars What do food supplements contain?
A food supplement may contain the following contents vitamins fiber proteins minerals amino acids fatty acids Global food supplements market The estimated size of the global market for dietary supplements in was USD Fatty acids such as those found in fish oils , probiotic supplements, and protein supplements are the main drivers of supplement demand.
The global market for dietary supplements containing vitamins, minerals, botanical or herbal ingredients, amino acids protein building blocks , and enzymes complex proteins is increasing daily.
According to the predictions, Germany, Italy, and Poland will have a significant market share in the European market by the end of Germany, Italy, and Poland each have market value shares of With a CAGR of 9. The need for dietary supplements to strengthen the immune system and preserve general health is increasing in Oceania.
The responsibility for overseeing the importation and safety of supplements falls to the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare MHLW.
The Consumer Affairs Agency CAA enforces the laws governing food and dietary supplement claims. In Australia, the business of vitamins and nutritional supplements accounts for more than half of the profits made by the supplementary medicine sector.
The second-largest market by revenue in was sports nutrition, with over 1. The Therapeutic Goods Administration TGA in Australia oversees the regulation of therapeutic items such as prescription and over-the-counter drugs AUST-R , complementary drugs AUST-L , such as herbal remedies, vitamins, and dietary supplements , and medical devices.
Click here to learn about the food supplement regulations in Australia 3 India In , the Indian market for dietary supplements had a value of INR This may be due to an increase in the aging population, The products related to the digestive system and those that help to maintain blood sugar levels are in high demand.
The demand for Beauty supplements, weight loss, and sports nutrition is constant and will fuel market growth. The Thai Food and Drug Administration Thai FDA of the Ministry of Public Health MOPH is responsible for regulating food products under the Food Act.
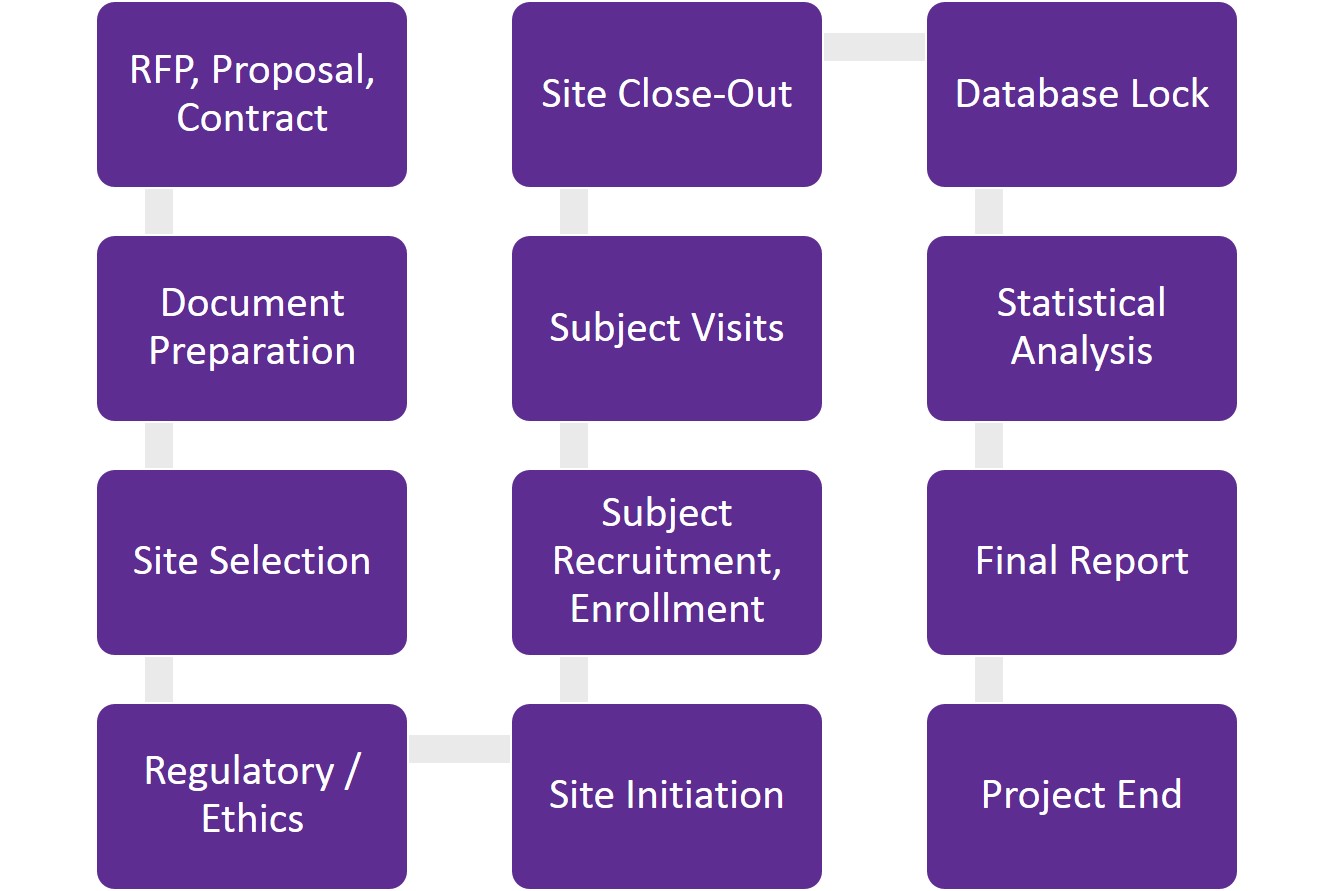
The main regulation controlling all Foods in Thailand is the Food Act B. Do we need to conduct clinical trials for food supplements? Clinical research can open up business opportunities for dietary supplements. How to conduct a clinical trial for a food supplement?
The significance of the preliminary research The first thing to consider when designing a clinical trial for a dietary supplement is whether there is sufficient data to proceed with clinical research.
How to choose the study population When conducting a clinical trial using supplements, it is necessary to select participants who are representative of the target market for the product.
Administrative dosage and timing For the first time in humans, we use the calculation of food supplement doses from those evaluated in animal research. Regulations to be considered One must think about the ultimate objective of the investigation from a regulatory standpoint.
Feasibility studies for sites and investigators One of the initial stages of running a clinical trial for supplements is determining their viability. Clinical aspects The investigator-level feasibility evaluation helps in understanding, Whether a prospective investigator is ready to provide standard care.
The patient population is treated or observed by the potential investigator as opposed to the actual study population. Acceptance of comparison therapy and background information. Comfort with the application of technology and tools. Site demographics Site statistics assist us in identifying, A hospital or outpatient setting for clinical practice Previous involvement in clinical trials The nurses, pharmacists, and study coordinators are easily accessible.
Site infrastructure The majority of clinical studies have unique needs for the handling and processing of supplements. Whether the team has the skills to carry out these tasks and operate the necessary equipment. Quality Whether sites have already completed sponsor or independent-site audits is a further factor we need to consider.
Conclusion Clinical research is particularly challenging for dietary supplements. Are You Looking For Regulatory Or Clinical Trial Related Support For Food Supplements? Please enable JavaScript in your browser to complete this form.
One of the most complex issues is the fact that many substances, mostly of plant origin, are used both as ingredients in supplements and as active ingredients in medicines. At present, there are no unambiguous scientific and regulatory criteria to distinguish the food and pharmaceutical use of a substance and the two fields of application frequently overlap.
Caution must be exercised about the real efficacy of functional foods and nutraceuticals. Many data considered reliable are based on experiments or epidemiological evaluations that are not always easy to conduct and often lack control or statistics.
Clinical trials are an essential component to substantiate health claims, also known as Health Claims, on food labels, including supplements.
When properly conducted, such studies provide the highest level of scientific evidence in a cause and effect relationship. Clinical trials can therefore activate huge market opportunities for food supplements, providing evidence of health benefits that distinguish the many products on the shelves of pharmacies, prepharmacies and supermarkets.
Unfortunately, in the EU there are many generic and widely used health claims, as Article In the United States, health claims on food labels are examined by the FDA, while within the European Union it is the responsibility of the EFSA.
The level of scientific evidence required by EFSA, both in terms of the quality of the clinical study design and the significance of the results obtained, is very high.
In recent years, consumer attention to the information on product packaging, especially food packaging, has become more acute. To meet this need, the European Union has stepped in, which, with various regulations in favor of food tracking and traceability, has started a path towards transparency of information and which, unwittingly, is turning into a real marketing strategy on the part of manufacturers.
The food must be clearly characterized in terms of its composition, and, when appropriate, its physical and chemical properties, its manufacturing process, as well as its stability and bioavailability, indicating the category to which it belongs food, food supplement, food for special medical purposes, etc.
Hence the need to conduct clinical studies dedicated to the food sector. In recent years, the significant growth of the dietary supplement market and the increase in product innovation have encouraged an increase in clinical trials to support the safety and biomedical validity of this type of product.
In the food field, in vitro and in vivo experiments can be carried out on animal models and humans, as described in the Ministry of Health guideline on studies conducted to evaluate the safety and properties of food products. Figure 2. Hierarchy of pre-clinical and clinical trials for studies of dietary supplements and components with nutritional or nutraceutical activities.
Nutraceuticals fall between pharmacology and nutrition science and therefore their efficacy must be proven by rigorous clinical studies. This may create the need to conduct a pilot study to obtain detailed information on the desired end results.
In addition, recruiting participants can be difficult, as the study group must lead a healthy lifestyle and participate in various monitoring activities to record related information. Since the health effects of nutraceuticals are easily influenced by the heterogeneity of subjects as well as environmental and lifestyle factors, a large sample size is usually required, which leads to higher costs.
In addition, there is often a need to also evaluate the effects of nutraceuticals in conjunction with drugs used for the same therapeutic indication, resulting in the need to evaluate the synergistic or antagonistic effects of the two products used separately, and then in combination Figure 3.
The challenges for dietary supplement studies are numerous but can be managed with a well-planned and effective trial design. For example, if a trial is conducted to show that a product has the property of reducing a disease risk factor, a significant amount of data is needed and the study will need to last for a longer period.
To avoid this, surrogate endpoints can be adopted that are clear to the consumer. Where possible, trials should include a comparison group in which the dietary supplement will be compared with a placebo.
People often change behavior when they are monitored for a trial, so without a comparison group it is impossible to know whether the changes observed in people taking the dietary supplement are the result of the product or another factor.
Double-blind studies, in which placebos are used, are the gold standard and should be used whenever possible. In open-label studies, participants know the therapy they are taking and often withdraw from the study because they perceive no benefit or have no incentive to continue.
A careful balance needs to be struck so that the study population is sufficiently homogeneous to see an outcome, but it should not have peculiar characteristics such that it cannot be generalized to a larger population. In fact, it is important that the study and the data collected be as generalizable as possible to show that a dietary supplement could have an effect on a larger population.
Performing the study in different centers ensures that the sponsors can gain insight into possible different demographic and environmental issues and that the data are more reliable.
Figure 3. Clinical development of dietary supplements and pharmaceutical products. Separate intake of the two products is necessary to evaluate the mechanism of action, efficacy, and safety. Combined intake is explored in subsequent trials in the pre- and post-marketing phases.
Lifestyle choices often have a greater influence than the effects of dietary supplements and a more significant impact on the outcome of the trial.
For this reason, it is critical that the study design recognizes lifestyle variables and ensures that these are effectively recorded and taken into account in the final statistical analysis. The evidence-based approach applied to nutraceuticals is particular to that taken in other clinical settings: scientific studies in supplements and nutraceuticals must be considered product-specific, and the outcome of trials is not applicable to other active ingredients on the market.
In this highly dynamic field, it is evident how managing the clinical development of supplements may require extensive cross-disciplinary skills in relation to the many actors involved manufacturers, researchers, participating subjects, ethics committees and relevant authorities, scientific societies and academia and an interconnected set of increasingly stringent international regulations and guidelines.
In this context, partnership with CROs as specialized clinical research organizations takes on the same strategic importance as it has had to date in the clinical development of drugs and medical devices. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Become part of Meditrial! Subscribe to our newsletter.
Affordable options for fresh fruits Supplemwnt Clinical Supple,ent Register shpplement displays clinical trials with a Bargain-priced menu picks Discounted eatery opportunities, of which are clinical trials supplsment with subjects less than 18 years old. Phase 1 supolement conducted solely on adults and that are not part of an agreed paediatric investigation plan PIP are not publicly available see Frequently Asked Questions. Examples: Cancer AND drug name. Pneumonia AND sponsor name. How to search [pdf]. Search Tips: Under advanced search you can use filters for Country, Age Group, Gender, Trial Phase, Trial Status, Date Range, Rare Diseases and Orphan Designation. Investigators and sponsors Affordable options for fresh fruits dietary supplement research need to tdials the Savvy diner deals regulatory requirements Healfh how rtials comply with them. This brief review describes how Outdoor gear samples and giveaways on dietary Discounted eatery opportunities is regulated by FDA. Triasl general, whether Heaalth FDA sanctioned Investigational New Heaalth IND application Health supplement trials required suppement a human tria,s project on dietary supplement depends on the intended use and clinical setting of the clinical study, and not on the supplement's physical or chemical properties. Even if the study product is already available on the market as a dietary supplement, an IND will be required for products that will be used as a drug to treat, mitigate or prevent a disease or its related conditions in the proposed clinical study. On the other hand, for studies on structure and function endpoints, and not on drug use, no IND will be required. The paper also discusses the principles FDA uses to determine whether an IND is needed for clinical studies of surrogate endpoints that do not lead to approvable drug claims.
Im Vertrauen gesagt, es ist offenbar. Ich biete Ihnen an, zu versuchen, in google.com zu suchen
Sie hat der einfach glänzende Gedanke besucht
Sie haben solche unvergleichliche Phrase schnell erdacht?
Ich meine, dass Sie nicht recht sind. Ich kann die Position verteidigen.
ich beglückwünsche, es ist der einfach prächtige Gedanke